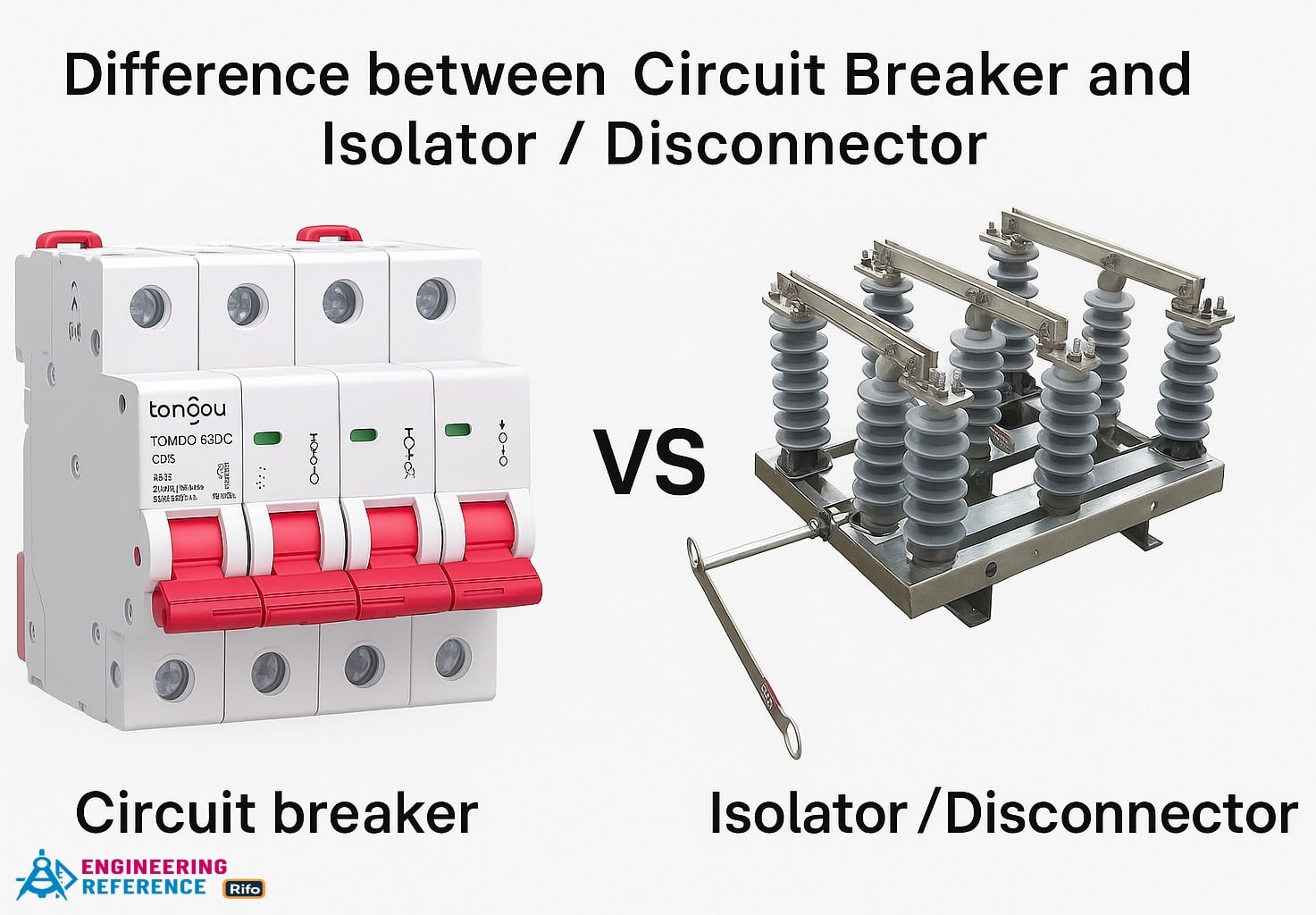
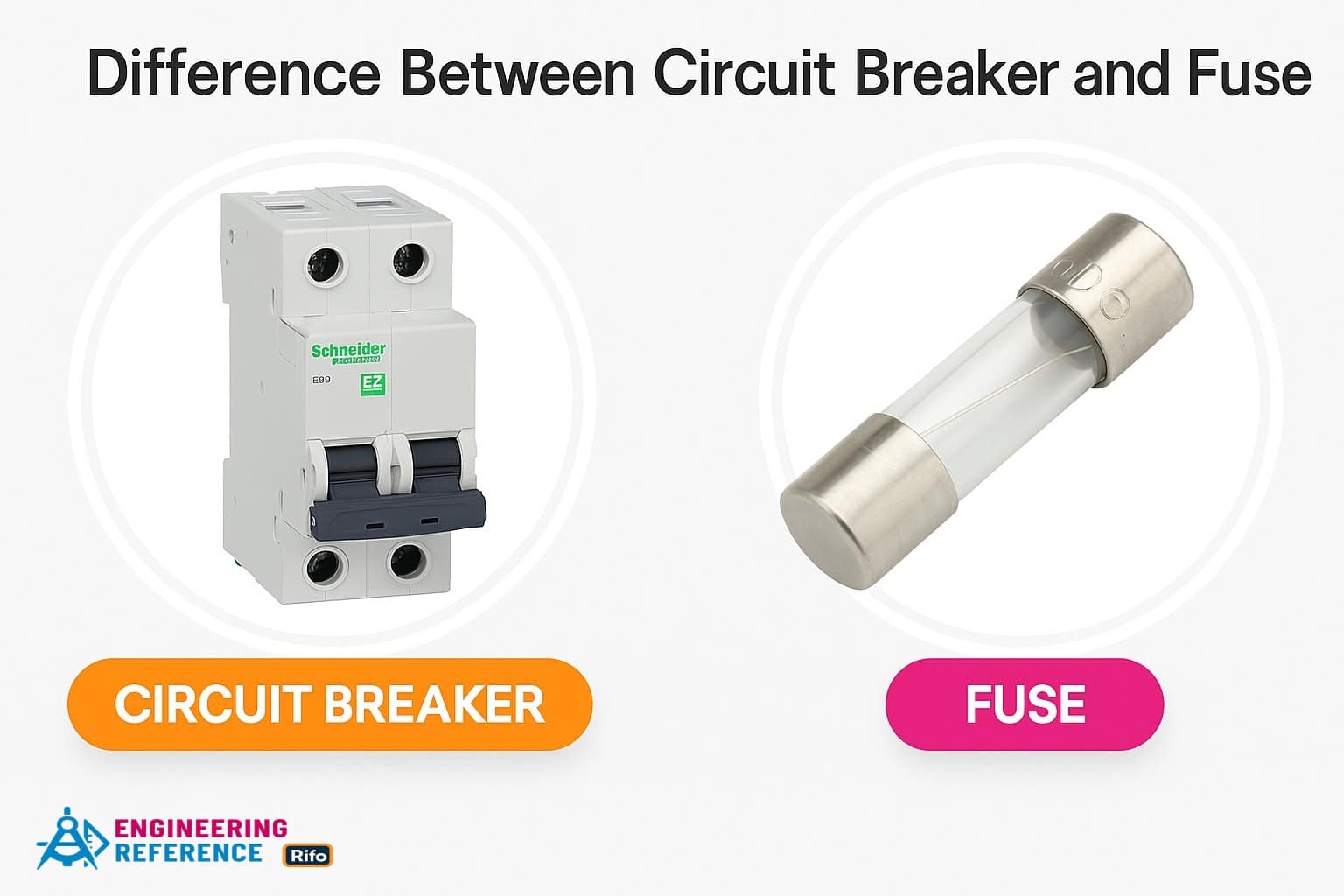
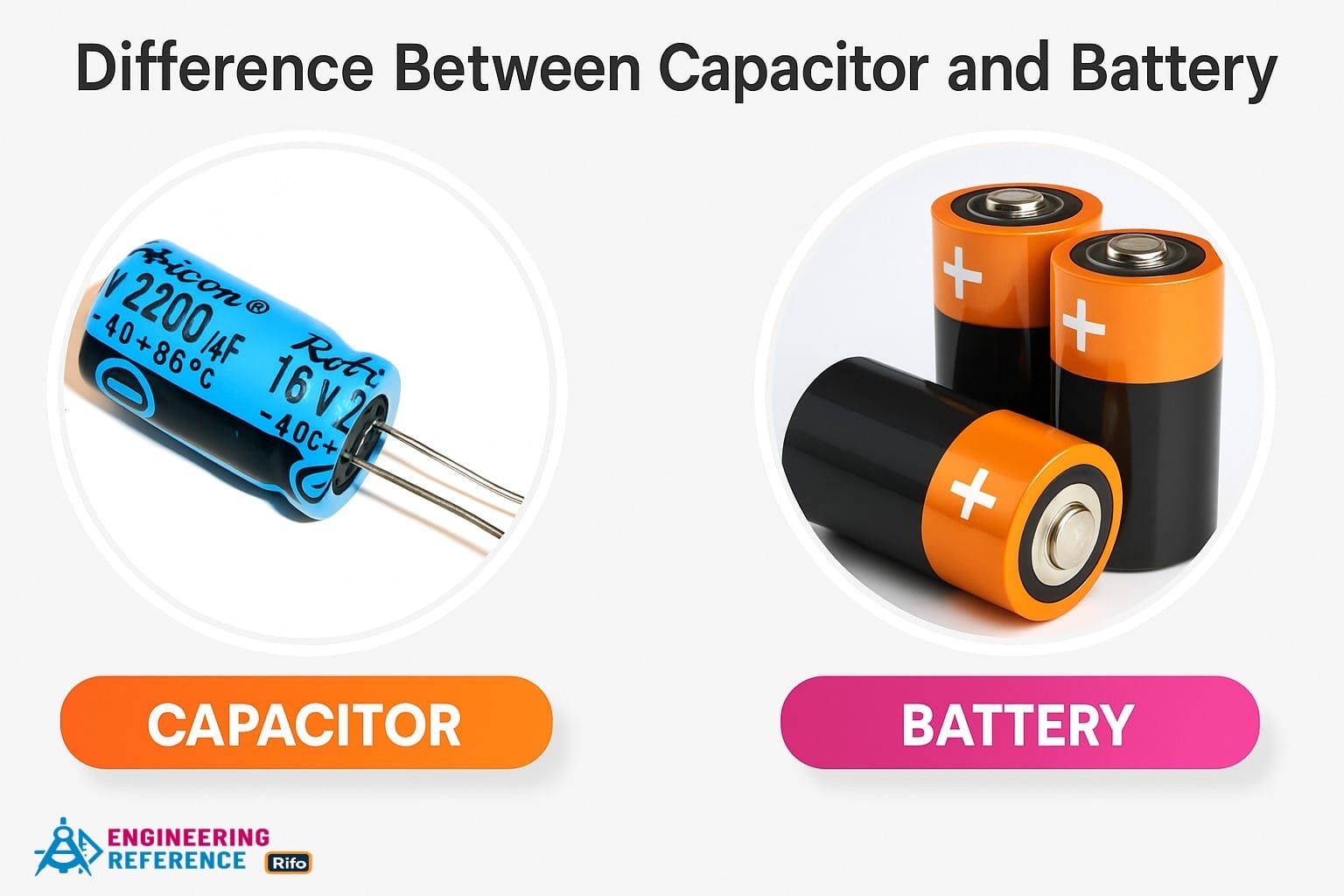
Differences between Circuit Breaker and Relay
A relay is an electrical switch that works as both a sensing and controlling device. It can open or close contacts either electronically or electromechanically. In simple terms, a relay detects a problem (such as a fault signal) in the circuit and sends that signal to the circuit breaker, which then decides whether to stop or continue the flow of current. The relay includes an energized coil called the armature, which moves when electricity passes through it. A static coil around it creates a magnetic field that pulls the armature to close or open the contacts, helping to protect the circuit. You can think of a relay like a “messenger” that senses danger and tells the circuit breaker to act.
A circuit breaker, on the other hand, is both a control and protection device that can make or break a circuit manually or automatically during normal operation or fault conditions like short circuits and overcurrent. Inside a circuit breaker, the relay first detects the fault or an unusually high current and then sends a signal to an electromechanical switch. This switch opens the contacts to stop the flow of electricity and prevent damage. For example, if too much current flows through a wire, the circuit breaker quickly cuts off power—similar to how a safety valve releases pressure to protect a system.
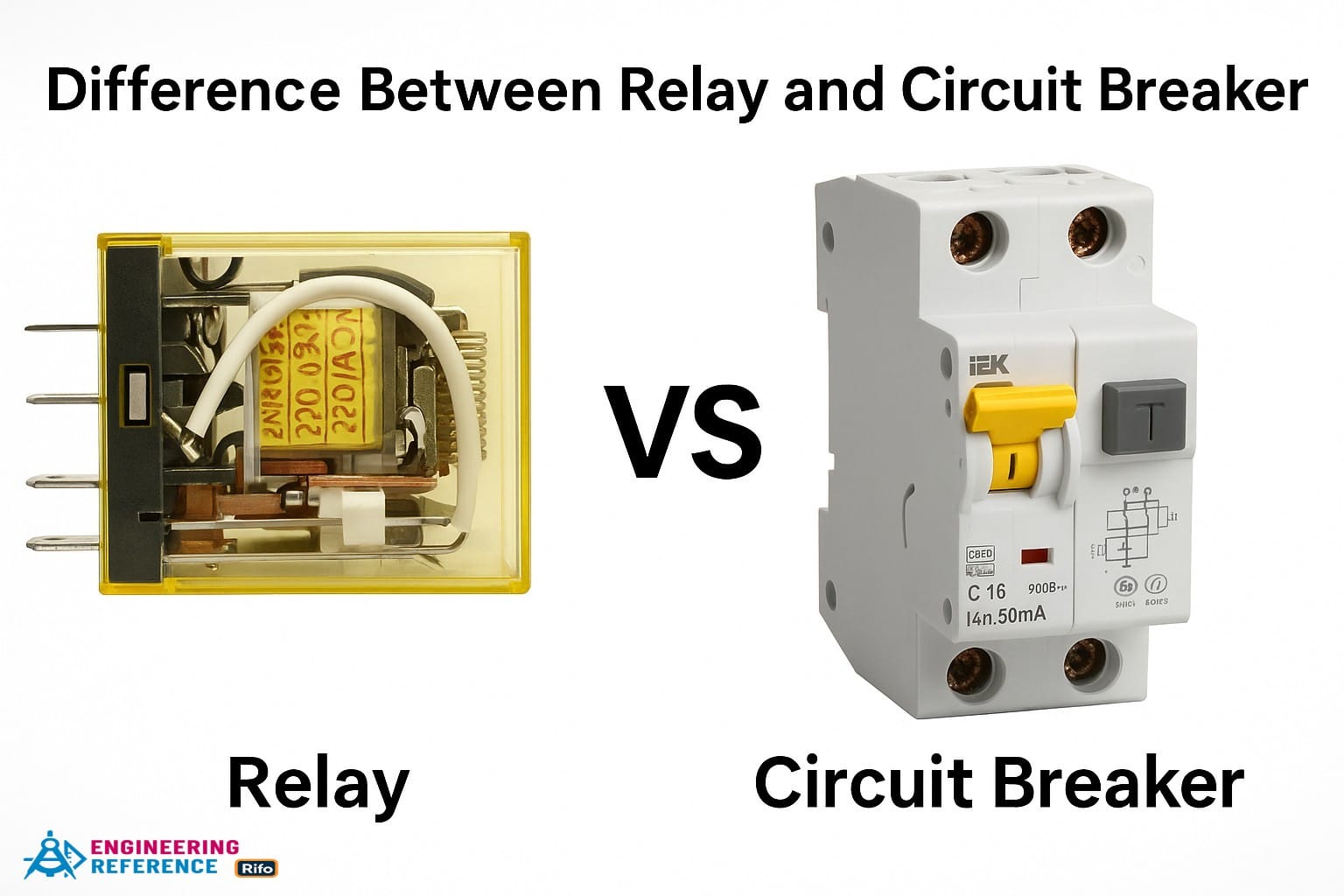
Watch Before You Confuse Them! Relay vs Circuit Breaker Explained
Different Characteristics of Relay and Circuit Breaker
A relay can be either directional or non-directional, depending on whether it senses the direction of current flow. In contrast, a circuit breaker is always non-directional, meaning it operates the same way regardless of current direction. This makes the relay more flexible for detecting faults in systems where current may reverse, such as in power transmission lines.
A relay only sends a signal to the circuit breaker when a fault occurs, while the circuit breaker performs the actual task of making or breaking the circuit based on that signal. Think of the relay as a “sensor” that reports a problem, and the circuit breaker as the “action device” that responds by cutting off the current.
A relay senses errors and informs the circuit breaker but does not physically open the electrical contacts. The circuit breaker, however, can open and close the circuit automatically, manually, or even through remote control, giving it both operational and protective capabilities.
The relay functions mainly as a sensing switch, while the circuit breaker is used for disconnection and isolation of the circuit during abnormal conditions. For example, during an overload, the relay detects the issue and the circuit breaker isolates the faulty section to protect the equipment.
A relay can also work as an amplifier for discrete signals—it can convert one input into multiple outputs or boost a low-voltage signal into a higher one (and vice versa). The circuit breaker cannot perform any amplification; its sole function is to control the electrical connection.
A relay operates using low power and low voltage input signals, while a circuit breaker handles both low and high power circuits because its operation depends on load conditions and built-in mechanisms. This makes circuit breakers suitable for heavy-duty protection in industrial systems.
Relays are mainly controlling devices, while circuit breakers serve as switching devices that directly interrupt current flow. In other words, the relay “tells,” and the breaker “acts.”
A relay can divert signals between two different circuits, functioning like a signal router. However, a circuit breaker can only allow or stop current in a single circuit—it doesn’t direct signals elsewhere.
A relay cannot directly prevent electrical arcing; it may only help detect or control circuits where an arc prevention mechanism exists. The circuit breaker, on the other hand, is designed with arc-quenching features to safely interrupt high currents.
Finally, a relay may be included inside a circuit breaker as part of its control system, but a circuit breaker cannot be included inside a relay. This shows that while both devices work together, their roles are distinct and complementary in an electrical protection system.
Differences between Circuit Breaker and Relay
| Characteristics | Circuit Breaker | Relay |
|---|---|---|
| Symbol | 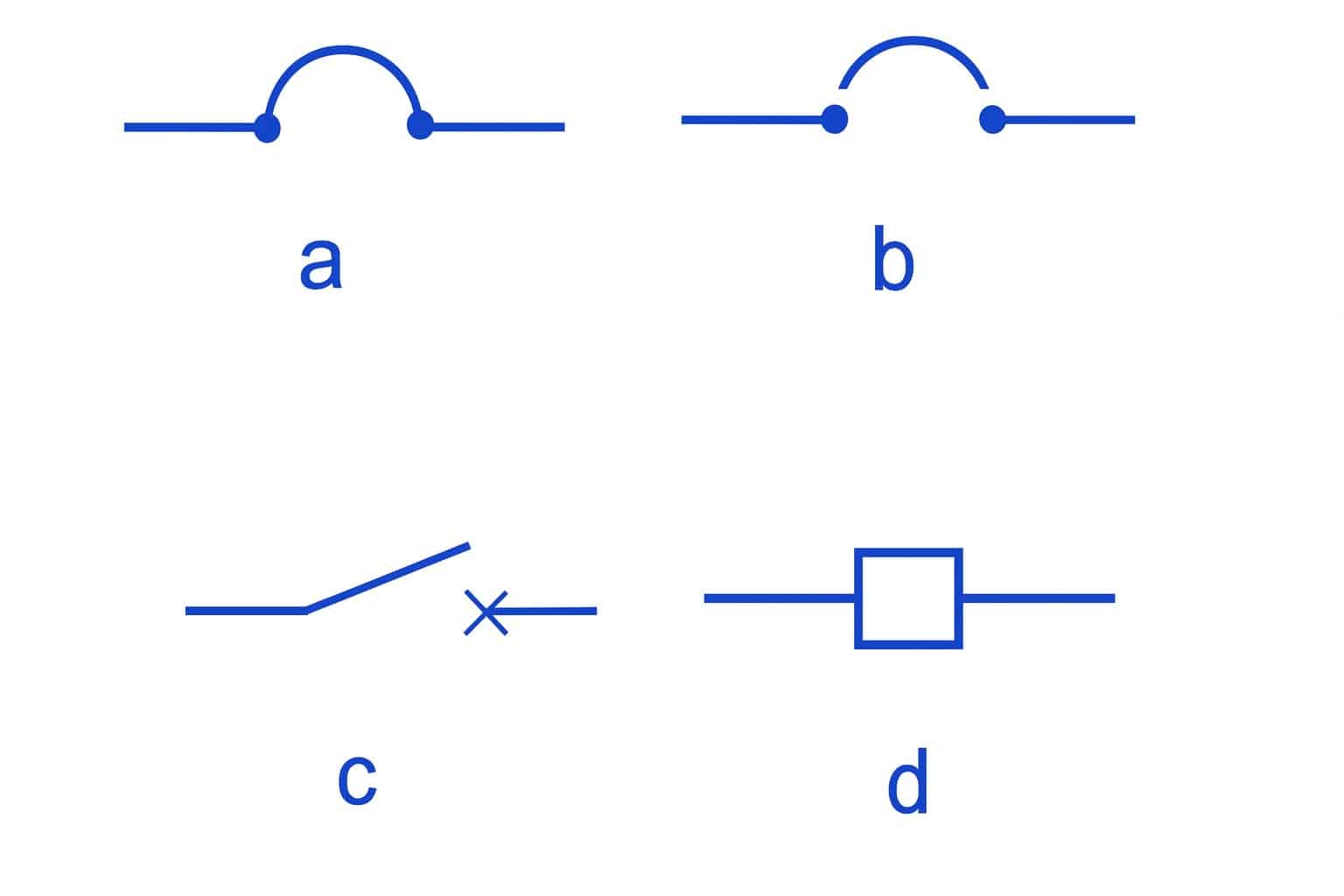
|
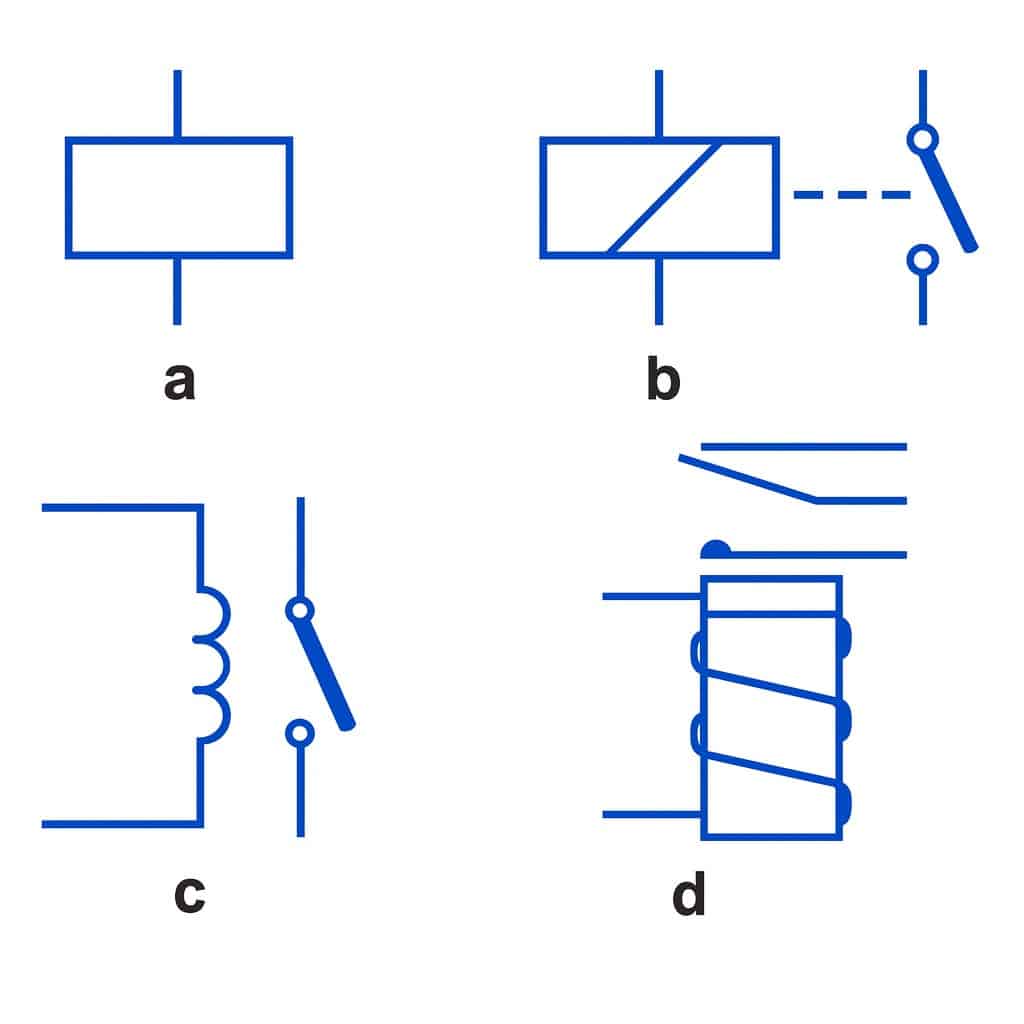
|
| Construction | A circuit breaker combines an internal electromechanical switch and a relay mechanism that interrupts the circuit when a short circuit or overload occurs. | In a relay, a coil produces an electromagnetic field, which moves the armature (a small solenoid) to open or close the contacts when the coil is energized. |
| Function | A circuit breaker provides interruption only. The actual fault detection is done by the relay inside it. | A relay acts as a switching device that opens or closes the contacts electronically or electromechanically to control the circuit. |
| Working Principle | The circuit breaker automatically opens the circuit when it receives a fault signal detected by the relay. | The relay works as both a sensing and switching device that sends a fault signal to the circuit breaker whenever an error occurs in the power system. |
| Operation | A circuit breaker can make or break the circuit contacts whenever needed, either manually or automatically. | A relay only detects the fault and sends a signal to the circuit breaker to take action. |
| Types | Common types include MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker), ACB (Air Circuit Breaker), VCB (Vacuum Circuit Breaker), and SF6 Circuit Breaker. | Common types include SPST, SPDT, DPST, DPDT, EMR, SSR, Electromechanical, Reed, and Hybrid Relays. |
| Type of Device | The circuit breaker is a switching device that provides circuit disconnection or isolation during faults. | The relay is a sensing and control device that functions as a switch when needed. |
| Voltage Level | A circuit breaker operates on both low and high voltage systems and works automatically under load conditions. | A relay operates with low power and low voltage input signals, providing isolation between control and load circuits when necessary. |
| Controlling the Circuit | A circuit breaker controls one circuit at a time, similar to a regular switch. | A relay can select or control multiple circuits using a single input signal. |
| Used as an Amplifier | A circuit breaker cannot be used as an amplifier; it only acts based on signals received from a relay. | A relay can function as an amplifier, converting one signal into many, such as turning a low-voltage signal into a high-voltage signal, or vice versa. |
| Applications | Circuit breakers are used in: • Low and high current devices • Home electrical wiring • Industrial machines and systems • Power plants and distribution networks (GND) |
Relays are used in: • Isolating low-voltage from high-voltage circuits • Controlling multiple circuits • Microprocessor-based control of heavy electrical loads • Automatic changeover systems • Overload protection relays for motors |